ArArCALC Help Library |
|||
1.5 Navigating and Flagging Data Points
ArArCALC is a visual tool that allows you to perform all functions with your Mouse, but also has many Keyboard Shortcuts that allow you to quickly activate certain functions. In this section, it is explained how to Navigate between the tables in your age calculation files, how to use your mouse in Flagging your analyses, and how to Delete your analyses, if so required.
1.5.1 Switch to ... Option
Switching from the Raw Data Reduction view to the Age Calculation view while saving your calculations is very simple. To do so, you should select the File # Switch to Age Calculation (Ctrl+Tab) menu option. Your calculations will be automatically saved (see also: Saving Data Reductions) and, if not possible, you will be notified with a warning. This functionality allows you to reduce your argon mass spectrometry data and then directly switch to the age calculations to check on the results. During this switching you can always suppress the saving, if you hold down the SHIFT key.
Switching from the Age Calculation view to the Raw Data Reduction view is very simple. To do so, you should select the File # Switch to Data Reduction (Ctrl+Tab) menu option.
1.5.2 Selecting Calculation Data Tables in ArArCALC
Nine different data tables are available in every ArArCALC age calculation file. Five of these tables include output data from your age calculations, whereas four tables include the input data necessary to perform the age calculations and which you can edit at any time (see also: Editing Data in ArArCALC). The calculation data tables are all located in the Data Tables worksheet and are selectable through the Tables menu. You can also use the F5, F6, F7, F8 and F9 keyboard strokes for faster navigation between the tables.
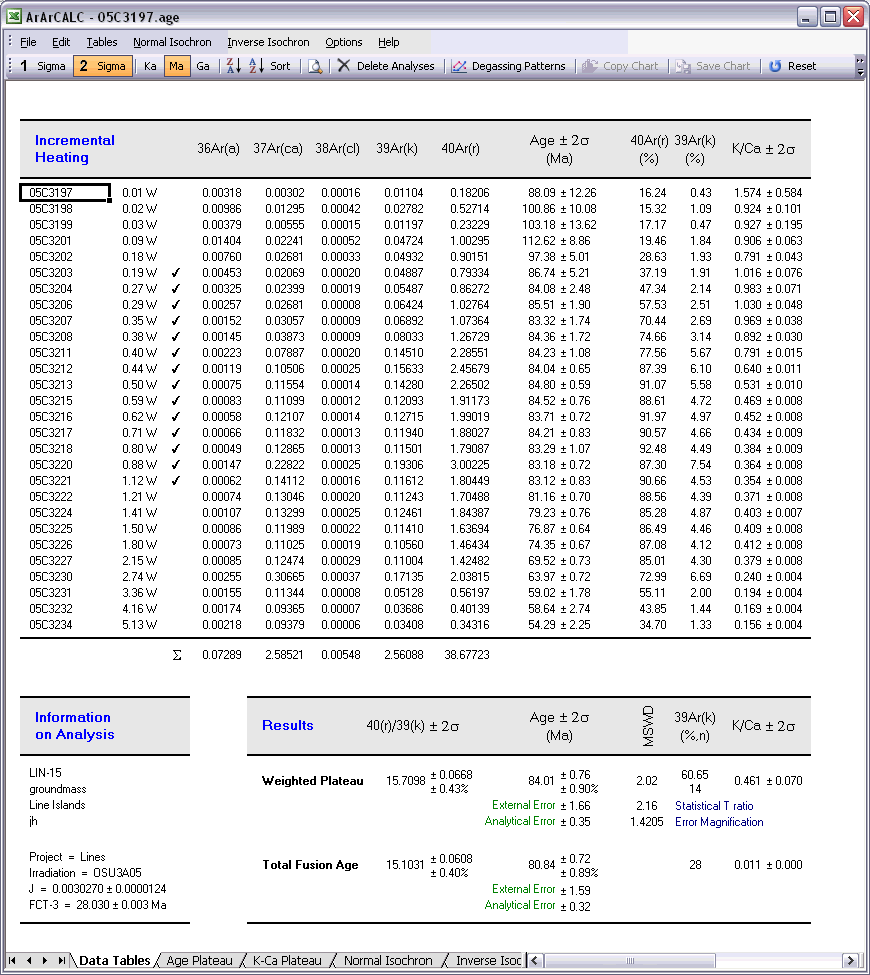
The Age Plateau data table contains calculation data for the plateau age, total fusion ages and K/Ca ratios. Note that also the MSWD, the number of increments and the total amount of 39Ar(k) in percent are given for the age plateau calculation. The uncertainties on the 40Ar/39Ar ages are defined as Internal Errors that combine the Analytical Errors with the Errors on the J-value. For completeness, the Analytical Errors and External Errors (including the error on the total 40Ar decay constant) are given as well (see also: Analytical, Internal and External Errors). The checkmarks signify the analyses included in the age plateau calculation, whereas the summed 36Ar(a), 37Ar(ca), 38Ar(cl), 39Ar(k) and 40Ar(r) components at the bottom of the table are used to calculate the total fusion (or recombined) age.
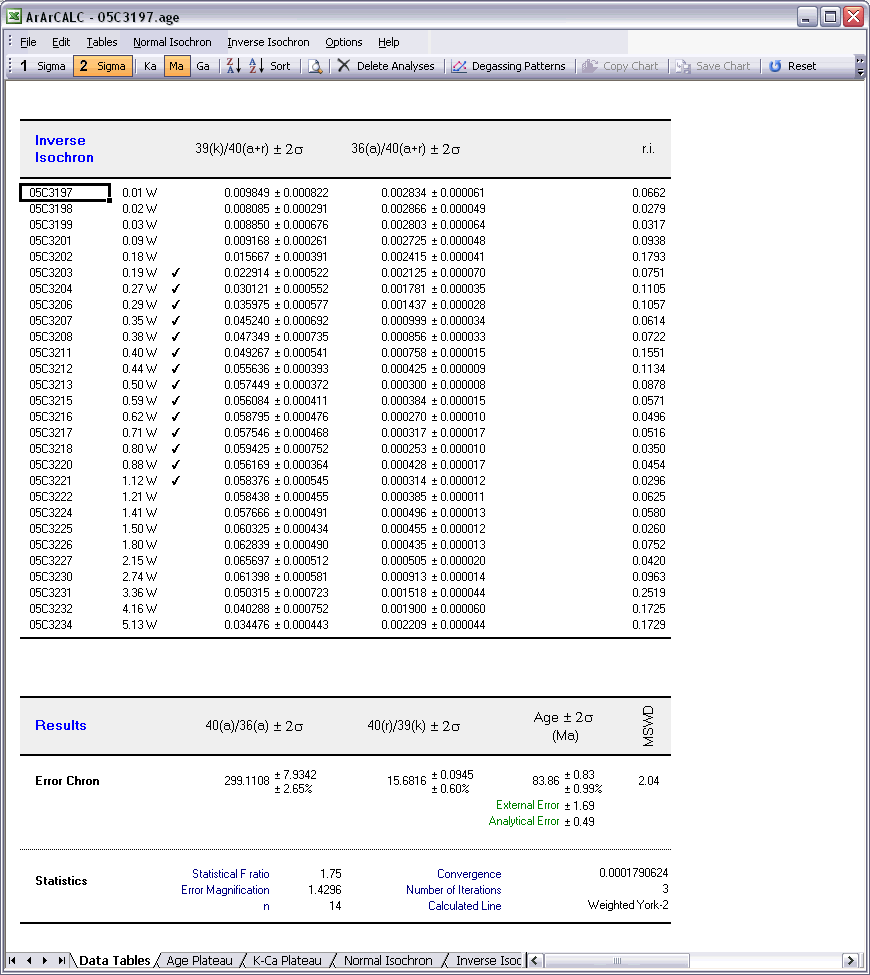
The Normal Isochron and Inverse Isochron data tables contain the calculated ratios 39Ar/36Ar, 40Ar/36Ar, 39Ar/40Ar and 36Ar/40Ar as used in the York (1969) isochron calculations. Both tables display correlation coefficients (r.i) denoting to what extend the errors used in these isotope ratios are correlated. In the example of an inverse isochron below, the correlation is minimal, because the error in the 40Ar (denominator) is small compared to the errors on 39Ar and 36Ar (the nominators). In the Statistics section the isochron calculations are further described by the convergence, number of iterations, type of calculated line, F-ratio, error magnification factor, and the number of points included in these calculations.
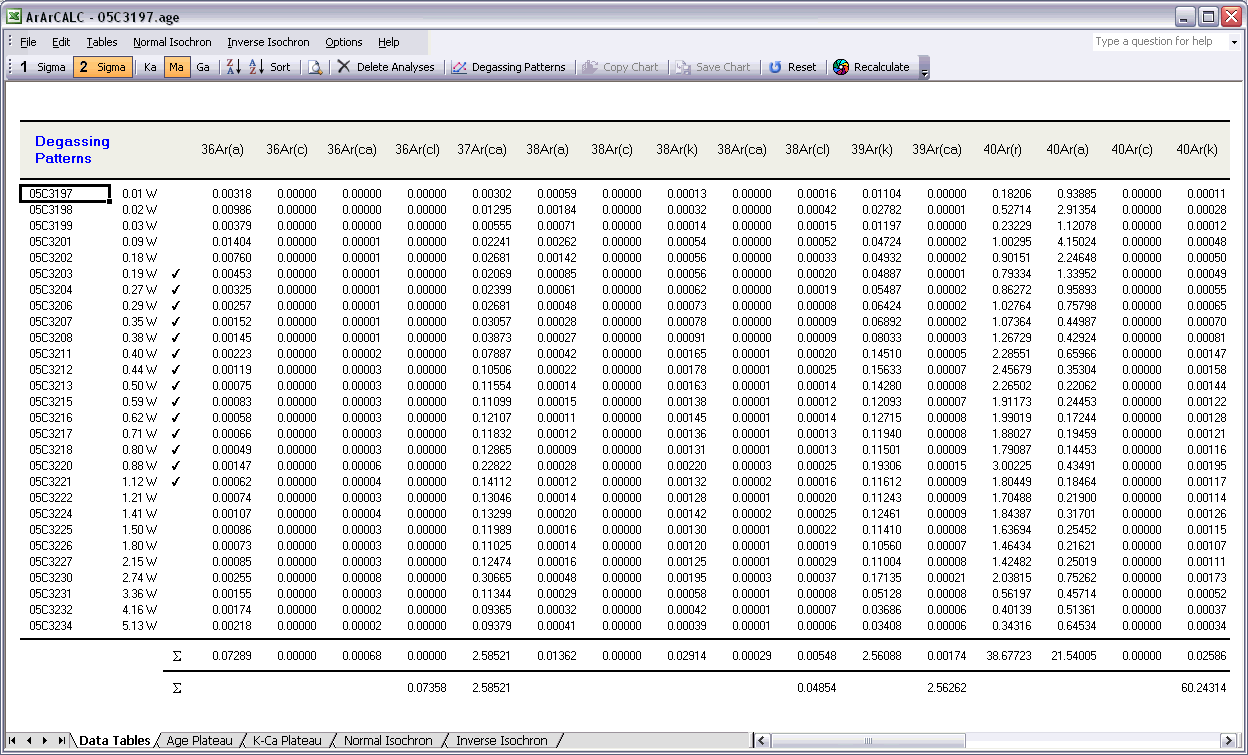
The Degassing Patterns data table contains for every analyses in your experiments the calculated argon components. For example, the entire measurement for the 36Ar isotope can be divided into the 36Ar(a) atmospheric, 36Ar(ca) calcium and 36Ar(cl) chlorine components, and if you are analyzing lunar rocks, also the 36Ar(c) cosmogenic component. For each individual component all increments or steps are summed, while the components themselves are summed as well (see the bottom of the table). A selection of these summed components appears in the Age Plateau data table as well (see above) and they are used to calculate the total fusion ages or to display these in the isochron diagrams (see also: Total Fusion Points in Isochron Diagrams). You can also visualize the Degassing Patterns in an interactive toolbox (see also: Degassing Patterns Toolbox).
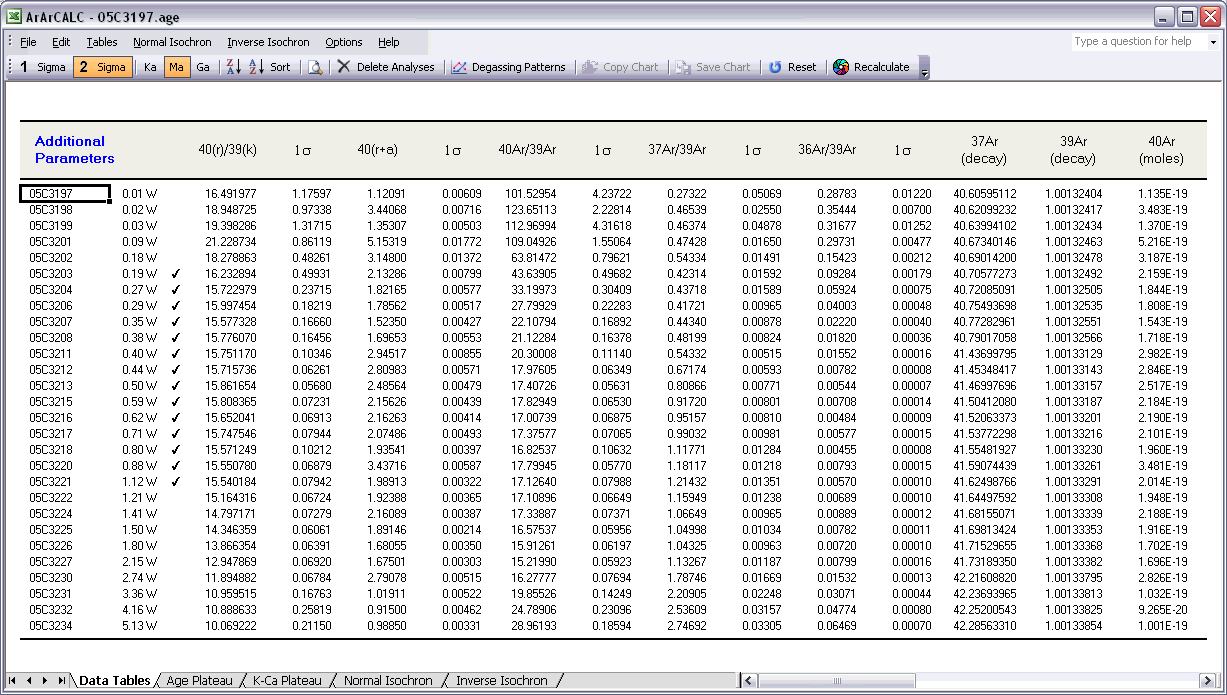
The last data table for Additional Parameters contains an extra selection of data that may be interesting to you when judging the outcome of your argon experiments. Most notable are the decay correction factors for 37Ar and 39Ar, which are used to correct for radioactive decay occurring between the irradiation of the sample and your actual measurements. But also the absolute amount of 40Ar measured is listed here in moles, and the corrected 40Ar/39Ar, 37Ar/39Ar and 36Ar/39Ar ratios and their uncertainties.
1.5.3 Editing Data in ArArCALC
Four data tables in ArArCALC include data necessary for the age calculations, but which you always can edit. These data tables are all located in the Data Tables worksheet and can be selected through the Edit menu. You can also use the F1, F2, F3 and F4 keyboard strokes for faster navigation between these tables.
ArArCALC has been set-up to run on-line during mass spectrometry and by default uses the latest-calculated blank measurement for its blank corrections. However, you can always edit the blank intensities later via the Edit # Procedure Blanks menu item. This function displays a data table containing Blank Intensities and their 1σ Standard Error (SE) for each analysis (step) in your (incremental heating) experiment. You can edit these blank data by clicking the cells and typing in new values. A single click lets you replace the complete number, whereas double-clicking will allow you to edit the number within its cell. To copy values from one cell to another, use the Drag functions of Microsoft Excel (drag the black square anchor visible on the highlighted cell down or to the right) or use the Copy (Ctrl+C) and Paste (Ctrl+P) buttons. Note that you can also copy blank values via the clipboard, in which case you select the cells in which to place your new values and use the Paste (Ctrl+P) button. The Reset button will undo all edits, unless you already have saved them.
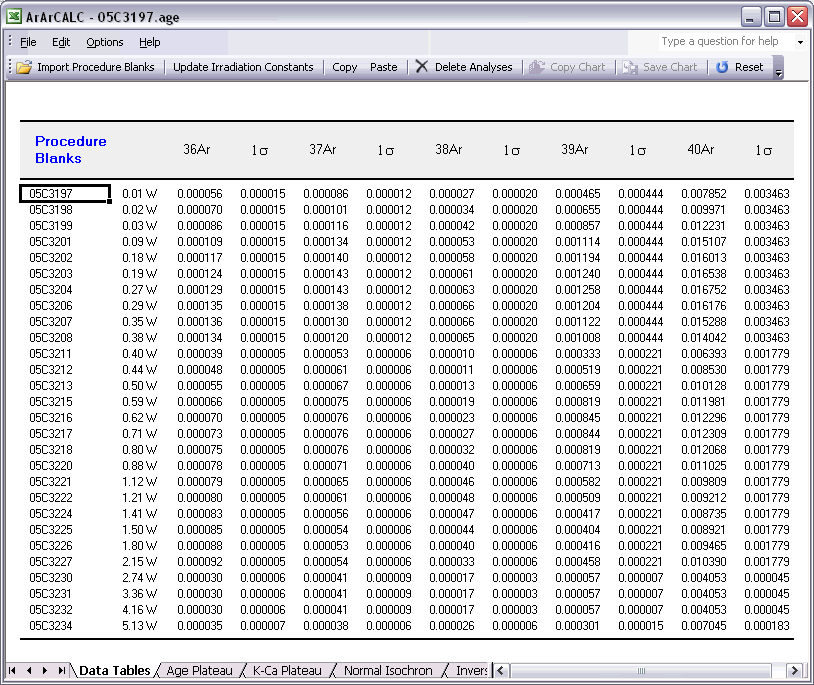
You can also select single (or multiple) cells, representing one (or more) analyses, and then choose Import Procedure Blanks from the toolbar. Since ArArCALC saves all blank measurements in text files organized per measurement date, this function allows you to import multiple blank measurements for a range of days, by opening more than one of these text files. Blank measurements can now be selected in the Select Blank Files list box to calculate Average Blanks for all argon isotopes, including their (predicted) standard deviations. This ArArCALC tool then automatically replaces all blank values and uncertainties in the edit table for the selected analyses. However, when the Default Errors checkbox is checked, the standard deviations will be overruled by percentual errors.
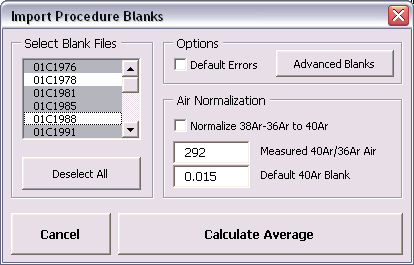
You can also click the Advanced Blanks button to analyze the Evolution in the Procedure Blanks over the same range of days. For each argon isotope you can now calculate a linear, parabolic or polynomial fit (pink dashed line). These calculations can be done while generating a standard error or 65-95% confidence envelop (grey dashed lines). The unknowns for which to calculate the blank values are indicated by gray circles at the bottom of the diagram (see also: Import Procedure Blank Toolbox). When you click the OK button, this ArArCALC tool again replaces all blank values and uncertainties in the edit table for the selected analyses.
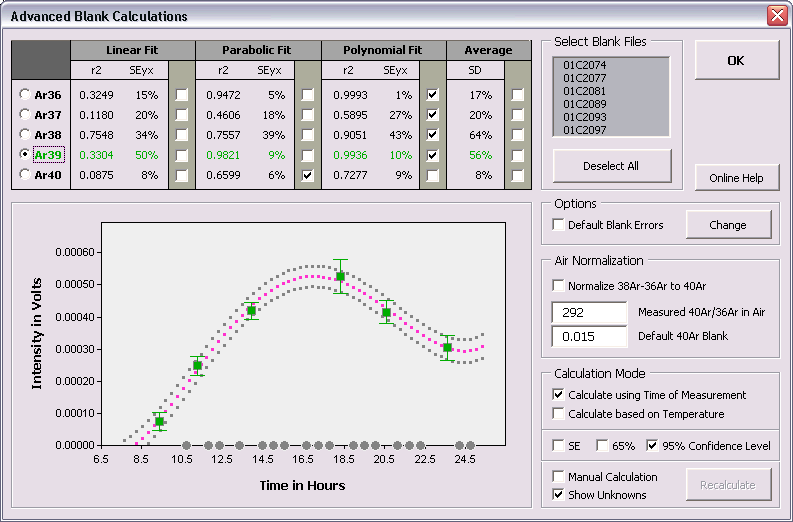
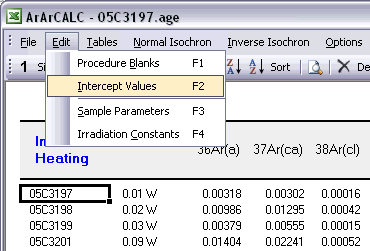
You can edit the intercept values via the Edit # Intercept Values menu item. In this data table all Intercept Values including their 1σ Standard Error (SE) are stored together with the r2, the type of line fit (EXP, PAR, LIN or AVE) and the data points excluded from the data regression. Editing is similar as described above. The Reset button will undo all edits.
The Sample Parameters (see also: Your First Calculations, Sample Parameters) can be edited via the Edit # Sample Parameters menu. This offers you the possibility to later finalize the actual J-value used in the age calculations or to better define the timing of the measurements. Note that in all the data tables the first two columns on the left (analyses number and increment temperature) cannot be edited. Although there is no possibility (and no need) to edit the analyses numbers, you always can adjust the temperature for each incremental heating step or analysis in the Temp column. All other values can be edited manually. The Reset button will undo all edits.
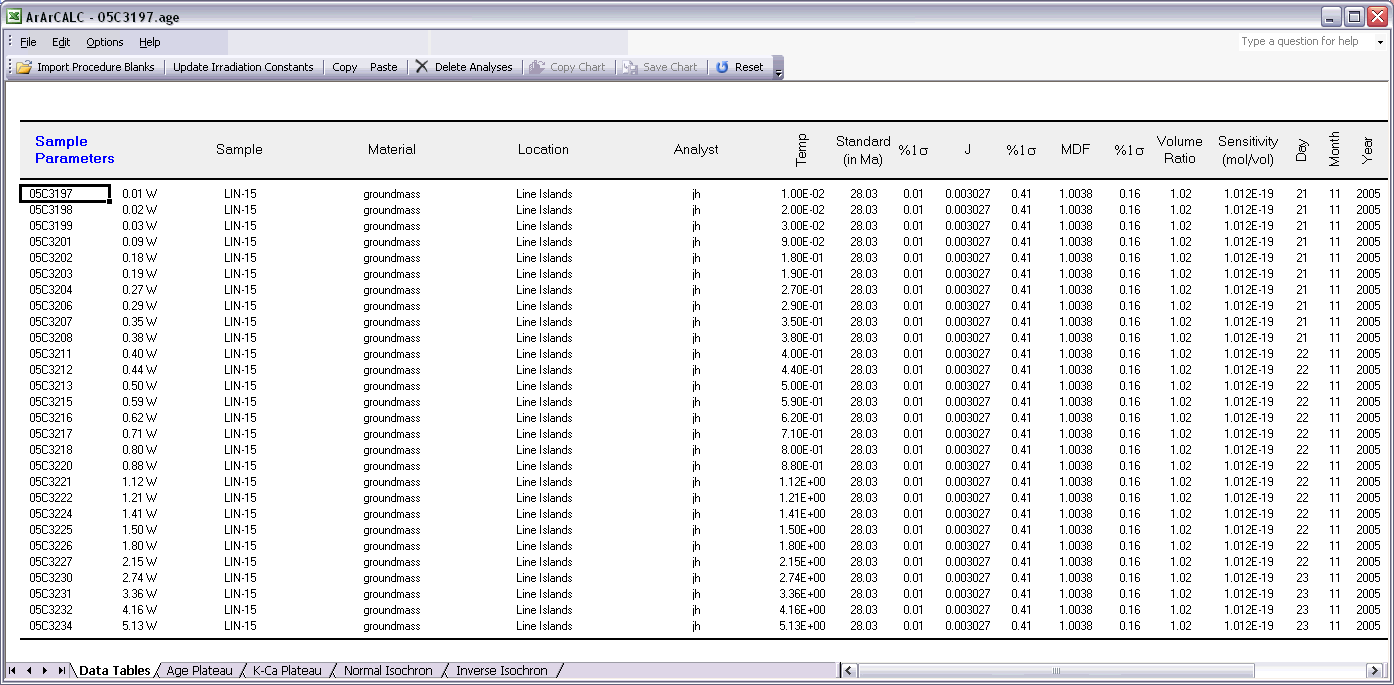
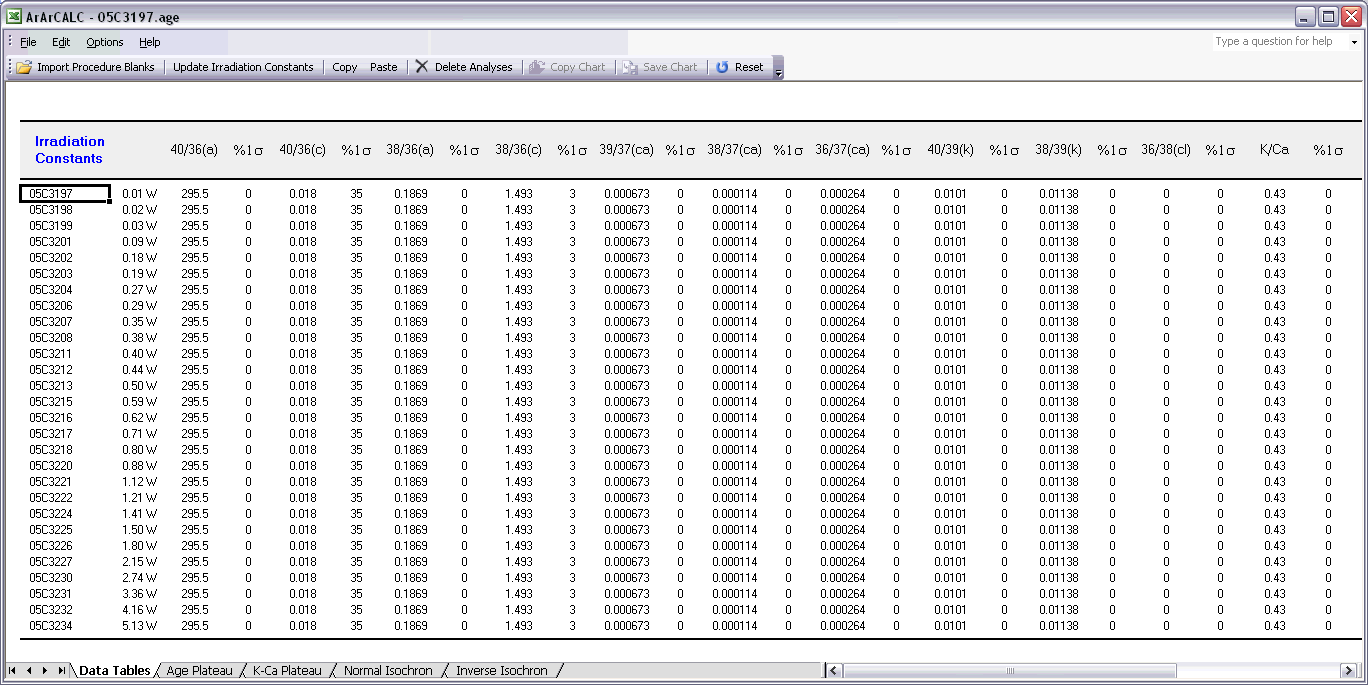
Finally, the Irradiation Constants may be edited via the Edit # Irradiation Constants menu item. This makes possible the combined age calculation of samples with different irradiation histories (see also: Import Additional Experiments). All irradiation constants can be edited manually. They can also be updated in one go by clicking the Update Irradiation Constants button, which will replace all values with the latest values found in the ArArCALC.log file (see also: Update Irradiation Constants). If you are going to calculate ages in the lunar mode, the labels of this table automatically will be changed from 40/36(a) to 40/36(t) and a default value of 40/36(t) = 1 is assumed (see also: Calculate as Lunar Sample). When you toggle back to the terrestrial age calculation mode, this value gets reset to the default 295.5 value for atmospheric argon. These are the only hard-coded values in ArArCALC and only are applied when toggling to lunar age calculations and back, but you always can overwrite these values by editing the Irradiation Constants table again. The Reset button will undo all edits.
1.5.4 Flagging Analyses in ArArCALC
Of course not every incremental heating experiment is perfectly concordant. So, you need to be able to easily Exclude discordant analyses (or steps) from your (incremental heating) experiments. On this help page three ways to do so are explained.
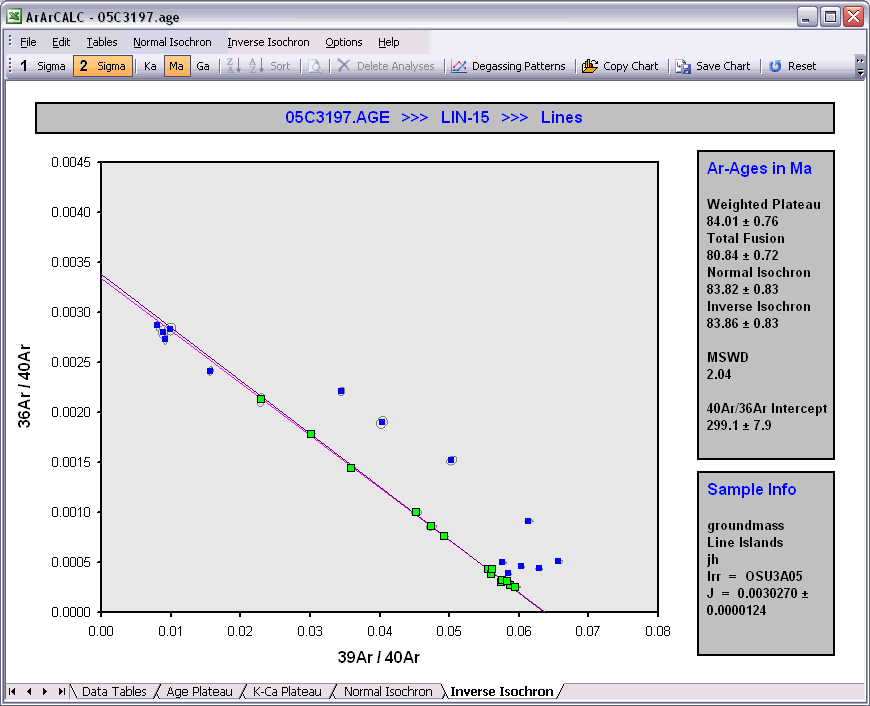
You can Flag Out your analyses for the age calculations in every data table by double-clicking the Checkmark symbols. When this action is performed ArArCALC recalculates all weighted averages and isochrons automatically, and updates all four diagrams. The total number of analyses included in the calculations are denoted in the Results panel (in this example, n = 14) as well as the total amount of released 39Ar(k) they represent (x = 60.65%). Flagging out multiple analyses is done by right-clicking every analyses that you want to exclude, ending by double-clicking the final one. Repeating these actions will include the analyses again. The Reset button recalculates including all data points.

Flagging Out analyses can also be performed by deselecting points in the isochron diagrams. You can simply do this by left-clicking the data points (green squares) in these diagrams, which change into blue squares when excluded. When this action is performed, ArArCALC recalculates all weighted averages and isochrons. ArArCALC will update all diagrams as well. Flagging out multiple analyses is done by right-clicking every data point that you want to exclude, ending with left-clicking the final one. Repeating these actions on the blue squares will include the analyses again. The Reset button recalculates including all data points.
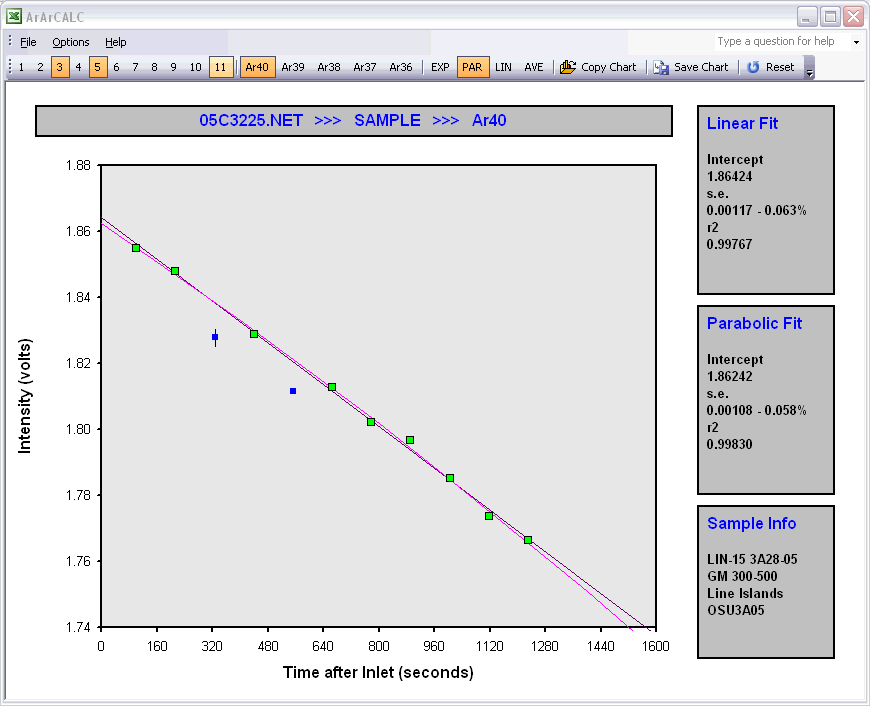
Raw Data Reduction Line Fit Diagrams
When you calculate line fits in the Raw Data Reduction view, you can exclude data points by either clicking the toolbar buttons 1, 2, 3 ... 11 that represent the data points or by left-clicking the single data points (green squares) on the diagram. Excluded data points are denoted by blue squares and suppressed toolbar buttons. Flagging Out multiple data points can be done by right-clicking each data point and ending with a final left-click. Repeating these actions on the blue squares or the suppressed toolbar buttons will include the analyses again. The Reset button recalculates including all data points.
1.5.5 Deleting Analyses from an ArArCALC File
You can delete analyses from the ArArCALC age calculations files at any time. This can be done from within all nine data tables. However, note that these age calculations files always should include at least two analyses. Select one cell or multiple cells (see below) representing the analyses that you want to delete, and select the Delete Analyses button from the toolbar. Before deleting the analyses, ArArCALC will ask you for a confirmation. ArArCALC will recalculate all ages and update all diagrams when the deletion is confirmed.
